Search engine indexing is how search engines like Google find, understand, and organise your website’s information. Think of it this way: for your site to even have a chance of showing up in search results, it first needs to be discovered and then filed away in a gigantic digital library. This "filing away" part? That's indexing.
Your Website's Entry into the Digital Library
Picture the internet as a colossal, ever-expanding library. To find a single book in that chaos, you’d need an incredibly efficient librarian who has catalogued every last one. Search engines are that digital librarian, and search engine indexing is their highly sophisticated cataloguing system.
Without indexing, a search engine would be forced to comb through trillions of web pages in real-time for every single search. That’s an impossible task that would take ages. Instead, it pre-organises everything it finds into a searchable database known as an index. So, when you search for something, Google isn't scanning the live internet; it's zipping through its own neatly organised index to give you answers almost instantly.
Indexing is the critical middle step between a search engine discovering your website and being able to show it to users. If your site isn't indexed, it simply doesn't exist in the eyes of a search engine, making it invisible to potential customers.
This process is what gives your website a ticket to the show. The infographic below breaks down the three core stages of search visibility, showing how crawling leads to indexing, which in turn makes ranking possible.
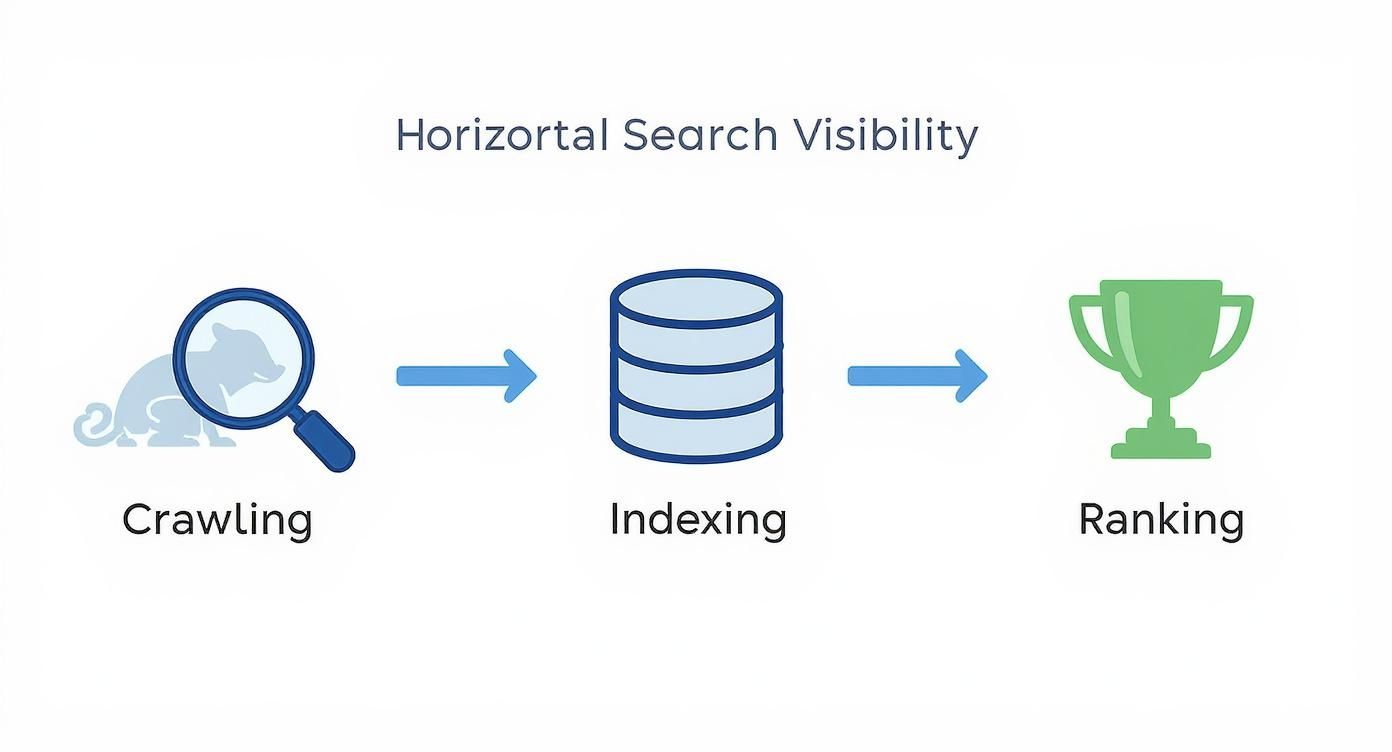
It’s a simple flow, but it highlights a crucial point: each step depends entirely on the one before it. If crawling fails, indexing never even gets a chance to happen.
The Three Pillars of Search Engine Visibility
For your website to get seen and start bringing in visitors, it has to pass through three distinct stages. Getting your head around these pillars is the first step to mapping out how your website actually gets found online.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what they are and why each one is so important.
| Stage | What It Is | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Crawling | The discovery phase. Search engine bots, or "crawlers," follow links across the web to find new and updated content. | If your site isn't found by crawlers, it can't move to the next stage. It’s the starting line for all search visibility. |
| Indexing | The analysis and storage phase. The crawler's findings are processed, and the content (text, images, etc.) is stored in a massive database. | This is where the search engine makes sense of your content. Without indexing, your site remains invisible in search results. |
| Ranking | The ordering phase. The search engine evaluates all indexed pages to decide which ones best answer a user's query and in what order. | This is the final goal. A good ranking puts your website in front of the right people at the right time. |
Each of these pillars builds on the last, creating the foundation for a successful online presence. It's a journey from being discovered to becoming a trusted result for potential customers.
In the UK, you can't really afford to ignore this process. Google holds a staggering 93.25% of the UK search engine market share, making it the undeniable gateway to British users. For UK site owners, if you're invisible to Google, you’re invisible to more than nine out of every ten potential customers. You can dig into more data on UK search trends over at Statista.
How Search Engines Find Your Website

Before a search engine can even think about indexing your website, it has to know it exists. This discovery process is the very first step, handled by tireless automated programmes we call crawlers or spiders. Think of them as explorers charting the digital wilderness.
These bots are constantly navigating the vast, interconnected web of links. They kick off their journey with a list of known web addresses from past crawls and sitemaps that website owners provide. From there, they follow links on those pages to uncover new URLs, effectively mapping the ever-expanding internet. This isn't a one-off event; crawlers revisit pages from time to time to see what's changed.
This journey is the absolute foundation of your online visibility. If a crawler can’t find your page, it can’t be indexed. If it’s not indexed, it will never show up in search results. A logically built website with clear, intuitive navigation is the perfect roadmap for these crawlers, making sure no valuable content gets left behind in some digital dead end.
The Crawler’s Main Pathways To Your Pages
So, how do these crawlers find their way to your content? They primarily stick to a few key methods. Understanding these pathways is crucial for making sure your pages are easy to discover.
A well-organised site makes their job incredibly efficient, allowing them to find and process your content without a hitch. The main discovery routes include:
- Following Links: This is their bread and butter. Crawlers jump from one page to another by following hyperlinks, both internal (links on your own site) and external (links from other websites).
- Reading Sitemaps: An XML sitemap is essentially a file you create that lists all the important pages on your website. Submitting it to search engines like Google is like handing them a precise map of your site.
- Discovering New Domains: Crawlers are always on the lookout for entirely new websites to add to their exploration list.
A crawler's job is purely discovery. It fetches the raw code of a page—the HTML, CSS, and other files—and sends it back for the next stage: indexing. It doesn't judge the content's quality; it simply finds it.
Guiding The Crawlers For Better Results
Believe it or not, you have a surprising amount of control over how crawlers interact with your site. By giving them clear instructions, you can point them towards your most important content and steer them away from pages you don’t want in search results, like admin login pages or internal documents.
One of the most powerful tools for this is a simple text file called robots.txt. Placed in your site's root directory, this file gives crawlers direct instructions on which parts of your site they can visit and which they should ignore. For a deeper dive into how this all works, our guide covers the robots.txt basics and what it does for SEO.
Getting this configuration right ensures that crawlers spend their valuable time on your most important pages, leading to much more efficient search engine indexing.
From Raw Data to a Searchable Index
Once a crawler has snatched the raw code from your webpage, the real work begins. This next stage is where search engines take that jumble of HTML and turn it into a neat, searchable entry in their colossal digital library. It’s a lot more involved than just saving a copy of your page.
To make sense of your content, search engines first have to render the page. This just means they process all the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to see it exactly like a human would in a web browser. They look at everything from the text and images to the layout, trying to figure out what the page is all about and how useful it is.
The Power of the Inverted Index
At the heart of this whole operation is an incredibly clever database structure known as an inverted index. Think of it as a gigantic, meticulously organised glossary for the entire internet. But instead of listing websites and then the words on them, it does the exact opposite.
The inverted index maps trillions of individual words and phrases to the specific URLs where they pop up. This smart reversal is the secret sauce behind a search engine's lightning-fast speed. When you type something into the search bar, the engine isn't frantically searching the web in real-time; it’s just looking up your keywords in this pre-built index to instantly pull up a list of relevant pages.
The diagram from Google below gives a great visual of how indexing fits between crawling and the final step of serving up results.

As you can see, indexing is that crucial middle step where raw, discovered data gets processed and organised into something truly searchable.
Avoiding Confusion with Canonicalisation
One of the biggest headaches for search engines is duplicate content. It’s pretty common for the same page to be accessible through several different URLs (like with and without 'www', or with tracking codes tacked on the end). To avoid stuffing their index with identical pages, search engines use a process called canonicalisation.
This is the all-important step of picking out the single, main version of a page—the canonical URL—that should be indexed and ranked. All the other duplicate versions are then pointed towards this primary one, which consolidates their value and avoids any confusion.
Canonicalisation ensures that search engines have one clear, authoritative source for your content. It prevents duplicate content issues from splitting your SEO value across multiple URLs, which could otherwise weaken your page's ranking potential.
By accurately rendering pages, building a super-fast inverted index, and using canonicalisation to tidy up duplicates, search engines bring order to the web's chaos. Getting your head around these mechanisms, including how structured data helps this process, is a massive part of SEO. You can dive deeper into what schema markup is in our detailed guide.
Why Indexing Is Your SEO Foundation

We've covered the mechanics of crawling and indexing, but let's get down to brass tacks: why does any of this actually matter for your business? The rule is brutally simple. If your page isn’t in a search engine’s index, it can't rank for anything. It’s like it doesn’t even exist to potential customers.
Think about it. Every pound you pour into stunning web design, killer content, or sharp marketing campaigns is completely wasted if your pages can't get indexed. It's the silent killer of SEO efforts, rendering your most valuable online assets totally invisible.
Proper indexing is the master switch for your online visibility. It's what allows you to connect with people actively searching for what you offer, fuelling traffic, leads, and ultimately, sales.
The Direct Link Between Indexing and Revenue
Getting into the index is the first step. But climbing to the top of it is where the real magic happens. In the fiercely competitive UK market, visibility is everything. The average click-through rate for the #1 organic spot on Google in the UK is a whopping 27.6%. That number plummets to just 15.8% for the second position, showing just how vital that top spot is.
Even worse, only a tiny 0.63% of searchers ever click on results from the second page onwards.
Simply put: no indexing means no ranking. No ranking means no visibility. And no visibility means no clicks, no traffic, and no sales from organic search. It’s the pillar that holds up everything else in SEO.
It's shockingly easy for a simple mistake to derail this entire process. A developer might accidentally leave a 'noindex' tag on a key service page, making it invisible to Google overnight and cutting off a vital stream of customers. This is exactly why a solid grasp of technical SEO is crucial for any business.
Turning Visibility into Growth
Effective indexing is the bedrock of search engine optimisation. It directly impacts your ability to rank higher and pull in more organic traffic. Once your pages are being consistently and correctly indexed, you can start focusing on the bigger picture.
For anyone serious about implementing strategies to increase organic website traffic, getting the indexing right is non-negotiable.
Without a solid indexing foundation, your website is like a shop with the shutters down and the doors locked. Customers can't get in because they don't even know you’re there. Getting indexed is how you unlock those doors and invite everyone—search engines and customers alike—inside.
Alright, let's get down to the brass tacks. Understanding how indexing works is great, but knowing how to put that theory into practice is what actually gets your pages seen by search engines.
To make sure your site gets discovered, understood, and stored properly, you need to be proactive. It's all about giving search engines a clear map to follow and clearing any technical hurdles that could trip them up.
The good news? You’re in the driver's seat. A few core strategies can make a world of difference, making it much easier for crawlers to do their job and get your best content indexed faster. These steps are the bedrock of any solid SEO effort.
Create and Submit an XML Sitemap
Think of an XML sitemap as a detailed roadmap of your website, made just for search engines. It’s a simple file that lists all your important URLs, helping crawlers find pages they might otherwise miss while just following links.
Most modern content management systems can whip one up for you automatically. Once you have it, the next step is to submit it directly through Google Search Console. This platform is your direct line to Google, giving you a peek into how it sees your site.
Here’s a look at the Google Search Console dashboard, where you can manage your sitemaps and keep an eye on your indexing status.
This interface is packed with crucial data on your site's health, including reports that show you exactly which pages are in Google's index and which ones are stuck outside.
Refine Your Internal Linking Structure
One of the most powerful—and often overlooked—tools for improving indexing is a smart internal linking structure. Every time you link from one page on your site to another, you’re creating pathways for both users and search engine crawlers to follow.
Pages that get a lot of internal links, especially from heavy hitters like your homepage, are flagged as more important. This sends a strong signal to search engines that these pages deserve to be crawled and indexed quickly.
A strong internal linking strategy doesn't just help with indexing; it distributes 'link equity' throughout your site and keeps users engaged by guiding them to related, valuable content. It’s a win-win for SEO and user experience.
Optimise Your Technical SEO Foundation
Finally, a few technical factors have a massive say in how efficiently your site gets indexed. Getting these right can be a game-changer, and if you want to dig deeper, exploring resources like free AI SEO tools can offer some advanced help.
Keep a close watch on these key technical optimisations:
- Site Speed: A slow-loading site is a major turn-off for both users and crawlers. A speedy website is far more likely to get a thorough crawl.
- Mobile-Friendliness: With most searches now happening on phones, Google has shifted to mobile-first indexing. Your site must be responsive and a breeze to use on a mobile device.
- Robots.txt File: Double-check that your
robots.txtfile isn’t accidentally blocking crawlers from important parts of your site. It’s there to guide them, not build a wall.
Mastering these directives gives you a huge amount of control over how search engines interact with your content. It’s about being intentional, guiding crawlers to your best stuff while keeping them away from the pages that don’t need to be in the search results.
Troubleshooting Common Indexing Problems
Even with everything set up perfectly, some pages just seem to play hard to get, stubbornly refusing to show up in search results. When this happens, your first stop should always be Google Search Console (GSC), a brilliant free tool that’s like having a direct line to Google.
It's in GSC that you’ll find messages that can look a bit cryptic at first. But once you understand what they mean, you've got the key to figuring out what's gone wrong.
Decoding Common Indexing Statuses
When you pop a URL into GSC's inspection tool, you get a clear status report back. Some of the most common ones are often misunderstood, but they point to very specific problems you can actually fix.
- Discovered – currently not indexed: This one means Google knows your page exists but just hasn't got around to crawling it yet. This is pretty normal for brand-new sites or if Google has decided that crawling your page isn't a priority right now, which can sometimes be a subtle hint about its perceived quality.
- Crawled – currently not indexed: This status is much more telling. It means Google has paid your page a visit but, after having a look around, decided not to add it to its library. The most common culprit here is content that Google sees as thin, low-value, or too much like another page it already knows about.
A "Crawled – currently not indexed" status is a direct signal from Google about your content's quality. Think of it as an invitation to review and improve the page to provide more unique value, rather than just hitting the 'request indexing' button again.
Fixing these issues usually involves a bit of detective work. You need to get to the root of the problem before you can apply the right solution. Luckily, the best tool for the job is right there in GSC. For a more detailed walkthrough, you can learn how to fix index coverage errors in Search Console with our complete guide.
Using the URL Inspection tool in GSC gives you a page-level diagnosis, showing you precisely what Google sees. It’ll flag up critical problems like server errors that stop Googlebot in its tracks, or an accidental noindex tag that's basically a "do not enter" sign. By pinpointing the specific roadblock, you can clear the path and finally get your content seen.
A Few Common Questions About Indexing
To wrap things up, let's tackle some of the most common queries people have about search engine indexing. Getting these straight can help you diagnose issues and set realistic expectations.
How Long Does Indexing Take?
The time it takes for a search engine like Google to index a new page can vary from a few hours to several weeks. Key factors include your website's authority, how frequently it's crawled, and how easily the page is found through internal links.
Manually submitting the URL via Google Search Console can often give it a nudge and speed up discovery, but there are no guarantees.
Will Every Page on My Website Be Indexed?
Not always. Search engines aim to build a high-quality index, not a complete one. They might choose to ignore pages with thin or duplicate content, or those blocked by a robots.txt file or a "noindex" tag.
Ultimately, their goal is to present valuable, unique content to users, so they filter out anything that doesn't meet the mark.
A key takeaway is that crawling is discovery, while indexing is organisation. A bot finds your page by following links (crawling). Then, the search engine analyses and stores that page in its database (indexing). A page must be crawled before it can be indexed.
At Bare Digital, we turn indexing issues into ranking opportunities. If you're struggling to get your pages seen, let our specialists run a free SEO Health Check. We'll give you a clear, actionable plan to boost your visibility and drive real growth. Get your no-obligation proposal at https://www.bare-digital.com.








