A 301 redirect is a permanent "moved house" sign for your webpages. Think of it like the Royal Mail's redirection service for your website—it makes sure anyone trying to visit an old web address gets automatically sent to the correct new one, so they don't end up lost. Getting this right is absolutely crucial for keeping your site running smoothly during any kind of update.
Understanding 301 Redirects in Plain English

At its core, a 301 redirect is just a status code sent by your server that signals a permanent move. When you set one up, you’re building a seamless bridge from an old, outdated link to a new, relevant page.
This isn't just about making life easier for your visitors, though. For search engines like Google, that signal is fundamental. It tells them not just to forward the user, but also to transfer all the hard-earned authority—often called 'link equity'—from the old page to the new one.
Without that redirect, any links pointing to your old page would hit a dead end, throwing up a frustrating "404 Page Not Found" error. This breaks user trust and tells search engines the page has vanished, effectively wiping out its value and damaging your search engine optimisation (SEO) efforts.
The Core Function of a 301
A 301 redirect has a simple but powerful job: it maintains continuity. Whether you’re restructuring your website, rebranding to a new domain, or just tweaking a page's URL, a permanent redirect makes the transition invisible to the user. Its main jobs are to:
- Preserve SEO Value: It passes the vast majority of ranking power from the original page to its new home.
- Improve User Experience: Visitors are automatically sent to the right page without hitting a dead end.
- Update Search Engine Indexes: It tells Google to drop the old page from its search results and list the new one instead.
Making sure your new web addresses are set up correctly is a huge part of this. To get your pages ready for success, it's worth checking out our guide on how to optimise URLs for SEO rankings.
Why This Matters for UK Businesses
The 301 redirect is an essential tool for UK businesses looking to protect their SEO value during website changes. In a massive analysis of 6 million redirects, the single biggest reason for their use was sites moving from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS protocol—a common and vital upgrade for British businesses today. This one change accounted for around 4.6 million redirects alone.
The same study found that almost half of these redirects worked perfectly, proving just how effective they are at guiding both users and search engines to the right place.
Why 301 Redirects Are an SEO Lifeline

For anyone who’s serious about their website’s performance, a 301 redirect is much more than a bit of technical jargon. It’s a cornerstone of any solid search engine optimisation strategy. Moving or deleting a page without one is like tearing a chapter out of a book and expecting readers—and search engines—to magically find the new information. They won’t.
Over time, your pages build up authority. They earn links from other sites, people share them, and search engines come to trust them as valuable resources. To really get why 301 redirects are so vital, you need a basic grasp of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). These redirects are the tool that protects all that hard-earned trust.
Protecting Your Precious Link Equity
One of the most important ideas in SEO is link equity, often called 'link juice'. It’s the value or authority that passes from one page to another through hyperlinks. When a reputable website links to your page, it’s giving you a vote of confidence, helping you rank higher in search results.
A 301 redirect is essentially a permanent forwarding address for that link equity. It tells search engines, "Hey, all the authority and trust that belonged to the old page? It now belongs to this new one." It's the best way to transfer that power, stopping your rankings from tanking after you've changed your site's structure.
Without a redirect, all that link equity just vanishes. Any links pointing to the old URL now hit a dead end, and the SEO value they carried is lost for good.
A 404 'Page Not Found' error is a catastrophic dead end for both users and search engine crawlers. It signals that content has vanished without a trace, damaging user experience and immediately devaluing any backlinks that pointed to the original page.
Avoiding SEO Disasters Like Duplicate Content
Search engines don't like seeing the same or very similar content on multiple URLs. This duplicate content issue confuses their crawlers, forcing them to guess which version is the "real" one to show in search results. Often, this means both pages end up ranking poorly.
301 redirects are the perfect fix. For example, you might have pages accessible from a few different URLs:
http://www.yourwebsite.co.uk/pagehttps://www.yourwebsite.co.uk/pagehttps://yourwebsite.co.uk/page
By using 301s to point all versions to a single, authoritative URL (like the https non-www version), you solve the duplicate content problem. This makes it crystal clear to search engines which page to index and rank, boosting its overall SEO power. This is a core part of any robust strategy, and you can learn more by checking out our guide on what is technical SEO.
The Cost of Neglecting 301 Redirects
In the UK digital marketing scene, getting 301 redirects right is considered non-negotiable, especially during major website redesigns or migrations. Failing to map old URLs to their new homes can cause a catastrophic drop in organic traffic.
With a well-planned redirect map, you can preserve around 80-90% of the SEO value from your backlinks, effectively protecting your online presence. It all comes down to a careful process of matching old URLs to their new, relevant counterparts.
Ultimately, a 301 redirect is your guarantee of a smooth transition. It protects your search rankings, keeps the user journey seamless, and maintains the integrity of your website in the eyes of search engines.
When to Use 301 Redirects in Your Business
Knowing the theory behind a **301 redirect** is a great start, but understanding exactly when to use one is what really makes a difference. These permanent redirects are your best friends during common—but critical—website changes.
Using them correctly keeps your users happy and ensures search engines don't lose track of your valuable content. Think of them as the plumbing of your website, guiding traffic and authority right where they need to go without any leaks.
Migrating Your Entire Website
One of the most crucial times to use 301 redirects is during a complete website migration. This might mean moving to a new domain for a rebrand or just switching to a new hosting provider.
Trying this without redirects would be an SEO nightmare. All your old URLs would lead to dead ends, wiping out your search rankings and losing traffic from any existing links pointing to your site. A key use for 301s is during a move to a new host, which is covered well in this website migration guide.
A carefully planned set of 301s ensures every single old page points directly to its new home, transferring the vast majority of your hard-earned authority and giving visitors a seamless experience.
Upgrading to Secure HTTPS
Switching your site from HTTP to the secure HTTPS protocol isn't really a choice anymore—it's essential for user trust and a confirmed Google ranking factor. The catch is that this transition creates a brand new version of every single URL on your site.
For example, http://yourshop.co.uk becomes https://yourshop.co.uk. To stop search engines from getting confused by duplicate content, you need to implement site-wide 301 redirects. This tells Google to permanently favour the secure HTTPS versions, consolidating all your SEO value into one authoritative set of URLs.
Restructuring and Optimising URLs
As your business grows, your website’s structure will likely need to change, too. You might want to reorganise content into better categories or update your URLs to be more descriptive and SEO-friendly.
Imagine a British e-commerce shop changing a product URL from a meaningless string of numbers to something much clearer:
- Old URL:
yourshop.co.uk/products/item-82199 - New URL:
yourshop.co.uk/products/mens-wool-trench-coat
A 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one is non-negotiable. It makes sure anyone who bookmarked the old link or clicks on it from another site lands on the right page, and it tells search engines where to send the ranking power.
Consolidating and Pruning Content
Sometimes, the smartest move is to combine several weaker, similar articles into one definitive powerhouse guide. This process, often called content consolidation or 'pruning', helps focus your SEO efforts and improve the overall quality of your site.
If you merge three blog posts about "local SEO tips," "Google Maps for business," and "local keyword research" into a single, comprehensive guide, you must use 301 redirects. You'd redirect the URLs of the two retired articles to the new master guide. This funnels their combined link equity into one authoritative page, giving it a much better chance to rank.
How to Implement 301 Redirects: A Practical Guide
Understanding the theory is one thing, but knowing how to actually set up a 301 redirect is where the real power lies. Whether you’re a developer who’s comfortable editing server files or a marketing manager using a content management system (CMS), there’s a straightforward method for you.
This guide will walk you through the most common ways to implement permanent redirects. We'll cover everything from server-level configurations for Apache and Nginx to the user-friendly tools built into platforms like WordPress and Shopify.
Server-Side Redirects for Apache and Nginx
For those with access to their website's server, implementing redirects directly is often the most efficient and reliable approach. This is typically a job for developers or technical SEO specialists. Most UK web hosts run on either Apache or Nginx servers, and each has its own way of handling things.
Using the .htaccess File on Apache Servers
If your website is hosted on an Apache server, you’ll be working with a file called .htaccess. This is a powerful configuration file that lives in the root directory of your website, and adding a simple line of code is all it takes to create a redirect.
To redirect a single page, you'd add this line to your .htaccess file:Redirect 301 /old-page.html https://www.yourwebsite.co.uk/new-page/
A word of caution: be extremely careful when editing this file. A tiny mistake or a misplaced character can take your entire website offline. Always, always back up your .htaccess file before making any changes.
Configuring Redirects on Nginx Servers
For sites running on Nginx servers, the process is a bit different. You’ll need to edit the server's main configuration file, which is usually located in a directory like /etc/nginx/sites-available/. Unlike Apache, these changes often require you to reload the server before they take effect.
Here’s what a single-page redirect looks like in an Nginx configuration:location = /old-page.html { return 301 https://www.yourwebsite.co.uk/new-page/; }
This method is highly performant but generally requires administrator access to the server, so it's not something most non-technical users will be able to do.
Platform-Specific Redirects in Your CMS
If editing server files sounds like a recipe for disaster, don’t worry. Most popular platforms have built-in tools or trusted plugins that make implementing 301 redirects a simple, code-free process. For most business owners and marketers, this is definitely the way to go.
Implementing Redirects in WordPress
WordPress doesn’t come with a built-in redirect manager out of the box, but there are several excellent plugins that handle the job beautifully. These tools give you a simple interface where you just paste the old URL and the new one.
Here are some of the most trusted options:
- Redirection: A free, powerful plugin that does one thing and does it well. It even logs all the 404 errors on your site, making it easy to spot and redirect broken links.
- Rank Math SEO: This all-in-one SEO plugin includes a robust redirect manager. If you’re already using it to handle your search engine optimisation, the redirect feature is ready and waiting for you.
- Yoast SEO Premium: The paid version of the popular Yoast SEO plugin also includes a redirect manager that makes the process incredibly straightforward.
With these plugins, setting up a 301 redirect is as simple as filling in two boxes: the "Source URL" (your old link) and the "Target URL" (your new link). The plugin handles all the technical wizardry behind the scenes.
Using the Built-In Redirect Manager in Shopify
Shopify makes managing redirects incredibly simple with its built-in URL Redirects feature. This is a lifesaver for e-commerce stores that frequently update products or reorganise collection pages.
To create a redirect in Shopify, just follow these steps:
- From your Shopify admin dashboard, go to Online Store > Navigation.
- Click on URL Redirects, which you'll find just above the Menus section.
- Click the Create URL redirect button.
- In the "Redirect from" field, enter the old URL you want to move.
- In the "Redirect to" field, enter the new destination URL.
- Click Save redirect.
This simple, built-in tool empowers Shopify store owners to protect their SEO without needing any technical expertise. This is especially crucial during major changes like a site overhaul, a topic we cover in our detailed guide on website migration SEO. Getting these redirects right ensures your valuable product pages don't lose their hard-earned ranking power.
Choosing the Right Tool: 301 vs 302 and Canonical Tags
Picking the right signal for search engines is a huge part of good technical SEO. Get it wrong, and you can cause all sorts of headaches for search crawlers, leading to nasty issues like duplicate content or watering down your hard-earned link equity.
That's why it's so important to get your head around the different roles played by 301 redirects, 302 redirects, and canonical tags. While a 301 is a permanent move, it's just one tool in your belt. Each option sends a very different message, so choosing wisely is key to protecting your site's authority.
The 301 Redirect for Permanent Moves
As we've covered, the 301 redirect is basically a 'we've moved house' sign for the internet. It's a clear, permanent instruction that tells users and search engines a page has moved for good. All the SEO value and link juice from the old URL get passed over to the new one.
You'll want to use a 301 redirect when a change is final:
- You've permanently changed a page's URL.
- You're migrating your entire site to a new domain.
- You're switching from HTTP to the more secure HTTPS protocol.
The 302 Redirect for Temporary Changes
A 302 redirect is the temporary cousin of the 301. It tells search engines, "This page has moved, but it'll be back." Because the change isn't forever, search engines don't pass the link equity to the new URL, and the original page stays in the search index.
This makes it the perfect tool for when you need to divert traffic for just a short time.
A 302 redirect is ideal for A/B testing a new page design or redirecting users during short-term website maintenance. It allows you to temporarily send visitors elsewhere without damaging the SEO value of the original page.
The Canonical Tag for Duplicate Content
Now, the rel="canonical" tag is a different beast altogether. It isn't a redirect; it's more of a 'hint' for search engines. You place it in the HTML head of a webpage to tell crawlers which version of a page is the main, or "canonical," one when you have duplicate content kicking about.
This happens all the time in e-commerce, where one product might be found through multiple URLs because of things like filters or tracking codes. The canonical tag neatly bundles all the ranking signals into a single, preferred URL without actually redirecting the user anywhere. If you want to go deeper, you can learn more about what a canonical URL is and how to use it right.
Comparing 301 Redirects, 302 Redirects, and Canonical Tags
To make it even clearer, let's break down the key differences between these three crucial SEO tools. Each serves a distinct purpose, and knowing when to use which is vital for maintaining a healthy, well-optimised website.
| Attribute | 301 Redirect (Permanent) | 302 Redirect (Temporary) | rel='canonical' Tag |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Informs search engines a page has moved permanently. | Informs search engines a page has moved temporarily. | Suggests the preferred version of duplicate pages. |
| Link Equity | Passes ~90-99% of link equity to the new URL. | Does not pass link equity; original URL keeps its value. | Consolidates link signals to the canonical URL. |
| User Experience | User is automatically sent to the new page. | User is automatically sent to the temporary page. | User stays on the current page; no redirect occurs. |
| Common Use Cases | Site migrations, URL changes, HTTP to HTTPS. | A/B testing, short-term promotions, maintenance. | E-commerce filters, tracking parameters, syndicated content. |
| Search Index | New URL is indexed; old URL is eventually removed. | Original URL remains indexed. | Canonical URL is indexed; duplicates are ignored. |
This table should help you quickly decide which tool is the right fit for the job, ensuring you send the correct signals to both users and search engines every time.
The infographic below offers a simple decision tree to help you visualise which implementation method to consider based on your website's platform or server.
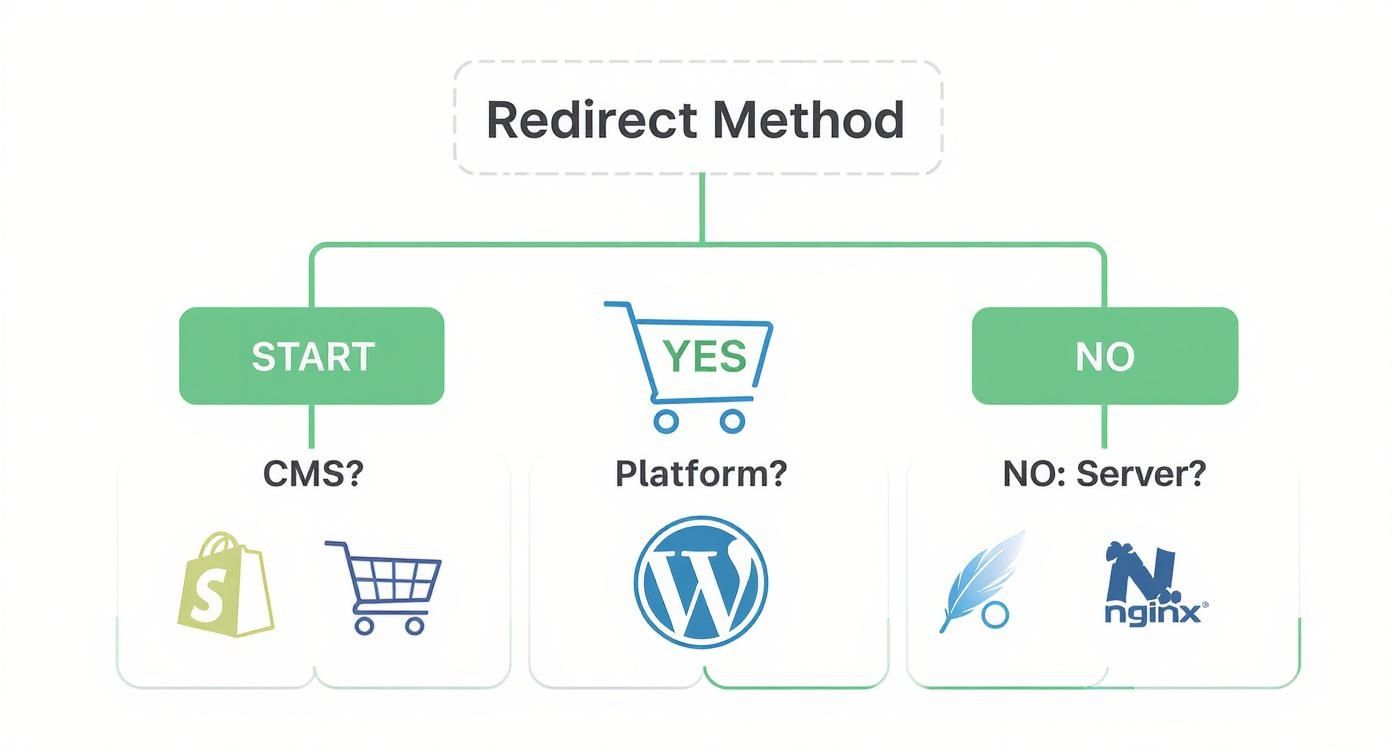
This visual guide breaks down the initial steps, making it clear whether you should be looking for a plugin on your CMS or getting your hands dirty with a server configuration file. By understanding these core differences, you can make smarter decisions that build a strong, healthy SEO foundation for your website.
Common Redirect Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

A 301 redirect is one of the most powerful tools in your SEO arsenal, but it's surprisingly easy to get them wrong. Simple mistakes can turn a helpful fix into a real headache, creating dead ends for your users and confusing search engine crawlers.
Getting redirects right from the start is non-negotiable. It protects your hard-earned rankings and keeps your website running smoothly. By sidestepping the common pitfalls, you can build a redirect strategy that just works.
Mistake 1: Redirecting Everything to the Homepage
When a page is removed, the easiest option seems to be pointing the old URL to the homepage. This is a huge mistake. Imagine clicking a link for a specific product review, only to land on a generic homepage. It's confusing, frustrating, and a surefire way to make someone hit the back button.
This kind of poor user experience sends all the wrong signals to search engines, and your rankings can suffer for it. The golden rule is simple: always redirect an old URL to the most relevant, similar page available. If there's truly no good alternative, it's better to use a 410 Gone status code. This clearly tells search engines the content was removed on purpose.
Mistake 2: Creating Redirect Chains and Loops
One of the worst technical SEO blunders is the redirect chain. This happens when Page A redirects to Page B, which then redirects to Page C, and so on. Each extra "hop" eats into your crawl budget and can dilute a small amount of your link equity. It's just inefficient.
Even worse is a redirect loop. This is where Page A redirects to Page B, but Page B mistakenly points right back to Page A. The browser gets stuck in an infinite circle until it eventually gives up, showing users an error. Search engines can't get past it, either, effectively blocking them from your content.
Your redirects should always point directly to the final destination. A single, clean redirect from the old page to the new one is the only way to go.
Mistake 3: Forgetting to Create a URL Map
Diving into a site migration or redesign without a proper URL map is like trying to build a house without a blueprint. It's a recipe for disaster. Before you touch a single thing, you need to create a spreadsheet mapping every old URL to its new home.
This URL map becomes your single source of truth, making sure no pages are left behind. It helps you:
- Audit all existing content: Figure out what to keep, combine, or delete.
- Plan new destinations: Carefully match old URLs to the most relevant new ones.
- Track your work: Use it as a checklist to confirm every redirect is implemented correctly.
Testing and Monitoring Your Redirects
Your job isn't done once the redirects are live. You absolutely must test them to catch any errors before they do real damage. Tools like Screaming Frog can crawl your entire site and flag any redirect chains, loops, or broken links that have slipped through the cracks.
You should also keep a close eye on the Coverage report in Google Search Console. This is where Google will tell you about any redirect errors its crawlers have stumbled upon, giving you a chance to fix them fast. Combine careful planning with regular monitoring, and you'll sidestep these common mistakes and get the full SEO benefit from your redirects.
Still Have Questions About 301 Redirects?
Even after you've got the hang of what a 301 redirect is, a few practical questions almost always pop up. Let's clear up some of the most common ones so you can manage your redirects with confidence.
How Long Should I Keep 301 Redirects in Place?
The short answer? Forever. If that’s not practical, think of one year as the absolute minimum. Google’s own experts have mentioned it can take well over a year for them to fully process a page move and pass over all of its ranking power.
Pull the plug too soon, and you risk the old URL popping back up in search results. When that happens, all the link equity you worked so hard to preserve simply vanishes.
Does a 301 Redirect Slow Down My Website?
A single 301 redirect adds a tiny delay that no user would ever notice. The real performance killer comes from redirect chains—when one URL redirects to another, which then redirects to another.
Each extra hop in a redirect chain adds noticeable lag to your page load time. This frustrates users and can harm your SEO. The best practice is always to point an old URL directly to its final destination, keeping things quick and clean.
Can I Redirect an Entire Domain with a 301 Redirect?
Absolutely, and you definitely should. A domain-level 301 redirect is the proper way to move an entire website to a new address permanently. This is usually set up at the server level, like in your .htaccess file.
It's a non-negotiable step in any rebranding or domain change project. It’s how you tell search engines to pass the vast majority of your old domain's authority and SEO value over to the new one.
What is the Difference Between a 301 and a 308 Redirect?
Both 301 and 308 codes tell search engines that a page has moved for good. The difference is a small technical one: a 301 allows the browser to change the request method (say, from POST to GET), whereas a 308 redirect forbids this change.
For most day-to-day SEO tasks, like redirecting a blog post or a product page, the 301 is the standard and works perfectly fine. You’d only really need a 308 in very specific technical cases where you must preserve the original request method.
At Bare Digital, we specialise in making technical SEO straightforward and effective for businesses across Cambridgeshire. If you want to ensure your website's performance is protected, get in touch for a free, no-obligation SEO Health Check. Visit us at https://www.bare-digital.com to start improving your online visibility today.








